EIRP
In radio communication systems, Equivalent Isotropically Radiated power (EIRP) or, alternatively, Effective Isotropically Radiated Power is the amount of power that a theoretical isotropic antenna (which evenly distributes power in all directions) would emit to produce the peak power density observed in the direction of maximum antenna gain. EIRP can take into account the losses in transmission line and connectors and includes the gain of the antenna. The EIRP is often stated in terms of decibels over a reference power emitted by an isotropic radiator with an equivalent signal strength. The EIRP allows comparisons between different emitters regardless of type, size or form. From the EIRP, and with knowledge of a real antenna's gain, it is possible to calculate real power and field strength values.
Features
- Measure Absolute Power Levels
- Upgrade to Spherical Near-Field Ranges
Datasheet
-
Applications
-
Compatibility
-
Includes
-
Related Technical Papers
- Windows® 7, 10
- NSI2000 Professional Edition
- EIRP Software
- Software Manual
- Estimating Uncertainties of System Level RF Parameters of Transponder Spacecraft Payloads
- A Dual-Band High Power PNF Range with Interleaved T R and Pulse Synchronization
- EIRP SFD Measurement Methodology for Planar Near-Field Antenna Ranges
- Measurement of Antenna Performance for Active Array Antennas with Spherical Near-Field Scanning
- Measurement of EIRP and Antenna Response for Active Antennas with Spherical Near-Field Scanning
- A Compact Antenna Test Range Built to Meet the Unique Testing Requirements for Active Phased Array Antennas
- Automated EIRP Measurements On A Near-Field Range

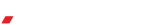
.svg?la=en&revision=cee9767f-8e72-4d76-a07a-14ba25688269&hash=ADF64722447408F8CA70B4436F59CB64)